A Short (But Exhaustive) Guide to SEO – Montreal
TL;DR:
- Publish quality content that is based on user intent
- Improve crawlability
- Improve page-speed
- Make the website mobile-friendly
- Implement schema markup
- Get backlinks and improve website’s authority
Why SEO Matters?
SEO drives traffic and conversions to a site by improving rankings and visibility in the organic search results.
What is on-site SEO?
On-site SEO is the practice of optimizing both the content and the code of a page in order to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic from search engines.
What is off-site SEO?
Off-page SEO involves improving site’s popularity, relevance, trustworthiness, and authority by linking or promoting website’s content.
1. Content based on user intent

Content is still king. If you’d like to rank you should be producing original, specific and thorough content that satisfies user intent. A recent study by backlinko looked at 11.8 million Google search results and found that quality content significantly outperformed content that didn’t cover a topic in-depth. Search intent is the why. Is a person searching for an information or are they looking to make a purchase?
If you can produce videos please do it. You will quickly climb at the top of the search food chain. If you can’t, then start a podcast and interview influencers. If you are good at graphic design then create infographics. Otherwise write or hire good writers. Finding a keyword or keywords that you want to rank for is easy. Just paste a topic into a keyword research tool and look for relevant keyword ideas with search volume.
You can start by asking yourself questions to identify the “3 C’s of content.” and looking at the top ranking search results.
- Content type: Are most of the results blog posts, product pages, category pages, landing pages, or something else?
- Content format: Is Google mainly ranking how-to guides, list-style articles, tutorials, comparisons, opinion pieces etc.? (Note. This one applies mainly to informational topics.)
- Content angle: Is there a common theme or unique selling point across the top-ranking pages? If so, this gives you some insight into what might be important to search.
You also have the option of looking at Search Engine Results Pages (SERP) features to get ideas.
Another way in which Google ranks the most reliable and useful results is by looking at content-related signals like expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. Collectively, these indicators are known as EAT.
(Learn more about EAT in Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines.)
Recommended reading:
2. Crawlability

Before search engines can even consider ranking your content, they first needs to know that it exists.
The leading search engines, such as Google, Bing and Yahoo!, discover new content with a web crawler, sometimes called a spider. A spider systematically browses the web, by following links, typically for the purpose of web indexing. The crawler processes both the text as well as the title tags, meta tags, and alt attributes for images.
You can see which pages are indexed by Google by using the search operator “site:yourdomain.com” (e.g., site:rushmediaagency.com) You can see how often Google is crawling your pages by looking at the Search Console. How often web crawler will crawl a site depends on the crawl budget.
You can submit a XML Sitemap to Google to ensure that all pages are found, especially pages that are not crawled through other links on the web. A sitemap is a list of URLs on your site that crawlers can use to discover and index your content. One of the easiest ways to ensure Google is finding your highest priority pages is to create a file that meets Google’s standards and submit it through Google Search Console.
You can use Screaming Frog to create an XML sitemap. Screaming frog is free if you are crawling a website that has less then 500 pages.
For WordPress users you can create an XML sitemap using Yoast.
Once you created your XML sitemap you can submit it in the search console.
Here is a great how-to article by Neil Patel on how to create and submit a sitemap.
Keep in mind that frequent indexing improves your search results.
That said, some things can block Google’s crawlers:
- Poor internal linking: Google relies on internal links to crawl all the pages on your site. Pages without internal links often won’t get crawled.
- Nofollowed internal links: Internal links with nofollow tags won’t get crawled by Google.
- Noindexed pages: You can exclude pages from Google’s index using a noindex meta tag or HTTP header. If other pages on your site only have internal links from noindexed pages, there’s a chance that Google won’t find them.
- Robots.txt: Robots.txt is a text file that tells Google where it can and can’t go on your website. If pages are blocked Robots.txt Google won’t crawl them.
Recommended reading:
3. Page speed

Pagespeed is a ranking factor on both mobile and desktop.
To check the speed of your web pages, use Google’s Pagespeed Insights tool, or Ahrefs Site Audit to check for slow-loading pages across your site.
- Compress images. Images usually take up to 50-80% of a page.
- Clean and compress the code, including HTML,CSS, JavaScript or any other code found on your page.
- Upgrade your hosting plan. If you’re serious about improving your site’s loading speed, it might be time to upgrade to a premium host or to a dedicated server.
- Activate Browser caching. Browser caching is a method of enabling browsers to save website data such as JavaScript, HTML, CSS, images and other files to improve the re-visit site performance. This won’t help your page load any faster for first-time visitors. But it’s great for improving your loading speed for people that have visited your site before.
- Implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN). A CDN refers to a geographically distributed group of servers which work together to provide faster delivery of Internet content. A CDN allows for the quick transfer of HTML pages, javascript files, stylesheets, images, and videos. Today the majority of web traffic is served through CDNs, including traffic from major sites like Facebook, Netflix, and Amazon.
2. Mobile-friendliness

Today over 63% of Google searches come from mobile devices, and 57% of internet users say they won’t recommend a business with a poorly designed website on mobile. To be noted however that during the pandemic this has dropped substantially in favor of PC and laptop searches.
In 2018 Google shifted to mobile-first indexing . This essentially means that it uses the mobile version of your page for indexing and ranking.
Here is a quick checklist for making sure your website is mobile friendly:
- Make sure your themes and sites are responsive. You can verify mobile-friendliness with the Google’s mobile-friendly testing tool.
- Don’t use pop-ups.
- Simplify your menus
- Keep forms as short as possible
- Make sure your CTAs are clearly displayed, and preferably use one CTA per page.
- Add a search bar to the home page to help improve navigation
5. Talk to robots with schema markup
Schema.org was launched in 2011 by Google, Bing and Yahoo to create and support a common set of schemas that helps the search engines understand the content of your website. Schema is still mostly an unexplored technique since only 12.29% of search queries have featured snippets in their search results. Also keep in mind that we are heading towards a voice dominated world. With Alexa, Siri and Google Home businesses and consumers are shifting from screen to voice while searching for and accessing information and 40.7% of all voice search answers come from a featured snippet.
Schema markup can generate rich results such as these:
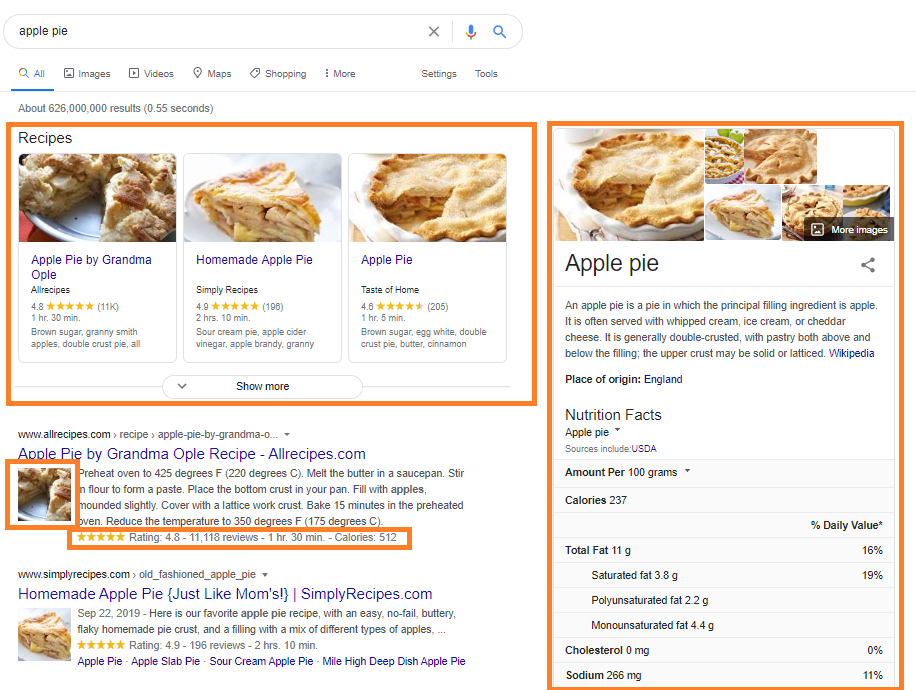
You can generate schema without knowing how to code schema.org language with Google’s Structured Markup Helper and import the code into the header of the page. Here is an article by Neil Patel on how to generate and implement schema on your website.
Here are the most common schema markup types:
- Organization
- Article, BlogPosting
- Reviews, Offer, Service
- Place, LocalBusiness, Restaurant
- Breadcrumbs
- Product, Offer, AggregateOffer
Schema should be implemented strategically. For example, if a blog post on a website is ranking well and is answering a question then implement an FAQ schema for that specific question. Here is a great article from Neil Patel about Featured Snippets.
5. Backlinks and Authority

In 1996, inspired by the citation impact that estimate the “importance” of scientific papers by looking at the number of other papers referencing them, Larry Page and Sergey Brin developed PageRank (PR). PR is an algorithm that counts the number and quality of links to a page to determine a rough estimate of how important the page is. A backlink is treated as a reference comparable to a citation and it’s weighting is similar to citation analysis of scholarly papers and academic journals.
Today, PageRank is not the only algorithm used by Google to order search results, but is still a core part of the ranking factors. A recent study by backlinko looked at 11.8 million Google search results and found that a site’s link authority strongly correlates with higher rankings.
Another ranking metric that became an industry standard is Domain Authority (DA) developed by Moz. DA is measured on a scale of 1 to 100. Moz has a free tool called Open Site Explorer (OSE) that you can use to check your DA.
In order to increase you PR or DA follow these steps:
- Do a link profile audit and disavow any unwanted links. You can use SEMrush backlink analytics or Ahrefs Site Explorer to analyze your backlink profile.
- Conduct a competitor backlink analysis. You can use SEMrush or a number of other tools to see the number and quality of sites linking to your competitors. If a competitor’s site is ranking well, you can look into it’s the backlink portfolio for opportunities.
- Solicit backlinks for your best content in person. You can use SEMrush link building email outreach tool.
- Improve your internal linking structure.
- Try broken link building.
- Write guest posts
- Build links by using a free service called Help a Reporter Out (HARO). HARO is the Tinder of public relations. It connects people that need sources journalists, bloggers and editors to people that want exposure and backlinks.
FURTHER READINGS
Final words
Knowing how search engines work and the factors they’re looking for when ranking content is a sure-fire way to create content that ranks and drive viewers to your page like moths to a flame.
It’s important to keep in mind, though, that search engine algorithms change all the time. There’s no guarantee that what is effective today will be so tomorrow.
Don’t let that panic you. As long as you’re consistent and dedicated you can stay ahead of the curve relatively easily.
Factors like backlinks, “authority,” and matching search intent have been critical factors for many years—and there’s no sign of that changing any time soon.
FURTHER READING
- Usefull SEO Links
- Local SEO Guide
- Schema Mark up Guide
- 9 EASY Link Building Strategies (That ANYONE Can Use)
- Resource Page Link Building: The Only Guide You Need
- How to Get Backlinks: 7 Tactics That Don’t Require New Content
- A Simple (But Complete) Guide to Broken Link Building
- 7 Actionable Ways to Loot Your Competitors’ Backlinks
- How to Get Backlinks By “Stealing” From Low-Quality Pages
- How to Execute the Skyscraper Technique (and Get Results)
